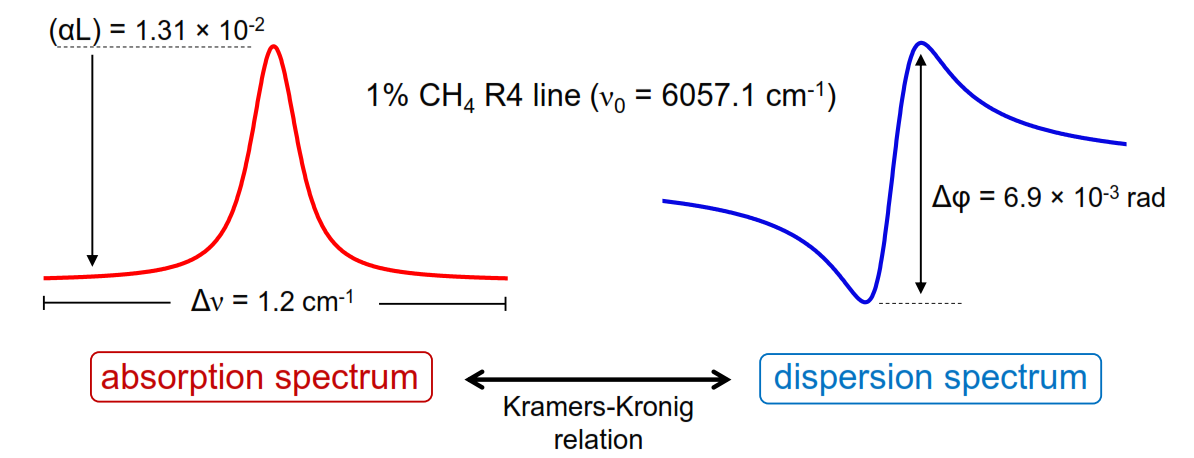
Laser spectroscopic techniques suitable for molecular dispersion sensing enable new applications and strategies in chemical detection. CLaDS (chirped laser dispersion spectroscopy) and its derivatives allow for quantitative spectroscopy of trace gases and enable new capabilities, such as extended dynamic range of concentration measurements, high immunity to photodetected intensity fluctuations, or capability of direct processing of spectroscopic signals in optical domain.
Projects:
- Optical-heterodyne-enhanced CLaDS
- Simultaneous ranging and remote sensing utilizing chirped laser dispersion spectroscopy
- Chirped laser dispersion spectroscopy using a directly modulated quantum cascade laser
- Distributed, fiber-coupled sensing
- Fundamental Noise Analysis in CLaDS
- CLaDS for Remote Open-Path Trace-Gas Sensing of Methane
- Chirped lasers dispersion spectroscopy implemented with single- and dual-sideband electro-optical modulators
- Chirped laser dispersion spectroscopy with harmonic detection of molecular spectra